You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to KubeVault? Please start here.
Deploy Vault on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Here, we are going to deploy Vault in AKS using KubeVault operator. We are going to use Azure Storage Container as Vault backend and azureKeyVault unsealer mode for automatically unsealing the Vault.
Before You Begin
At first, you need to have an AKS cluster. If you don’t already have a cluster, create one from here.
Install KubeVault operator in your cluster following the steps here.
You should be familiar with the following CRD:
You will need a storage account. Guides to create a storage account can be found here. In this tutorial, we are going to use
vaultstorageacstorage account.You will need a Azure Storage Container to use it as Vault backend storage. In this tutorial, we are going to use
demo-vaultblob container invaultstorageacstorage account.You will need a Azure Key Vault for unsealer. Guides to create key vault can be found here. In this tutorial, we are going to use
vault-key-storekey vault.
Provision Cluster
We are going to provision Kubernetes cluster using AKS.
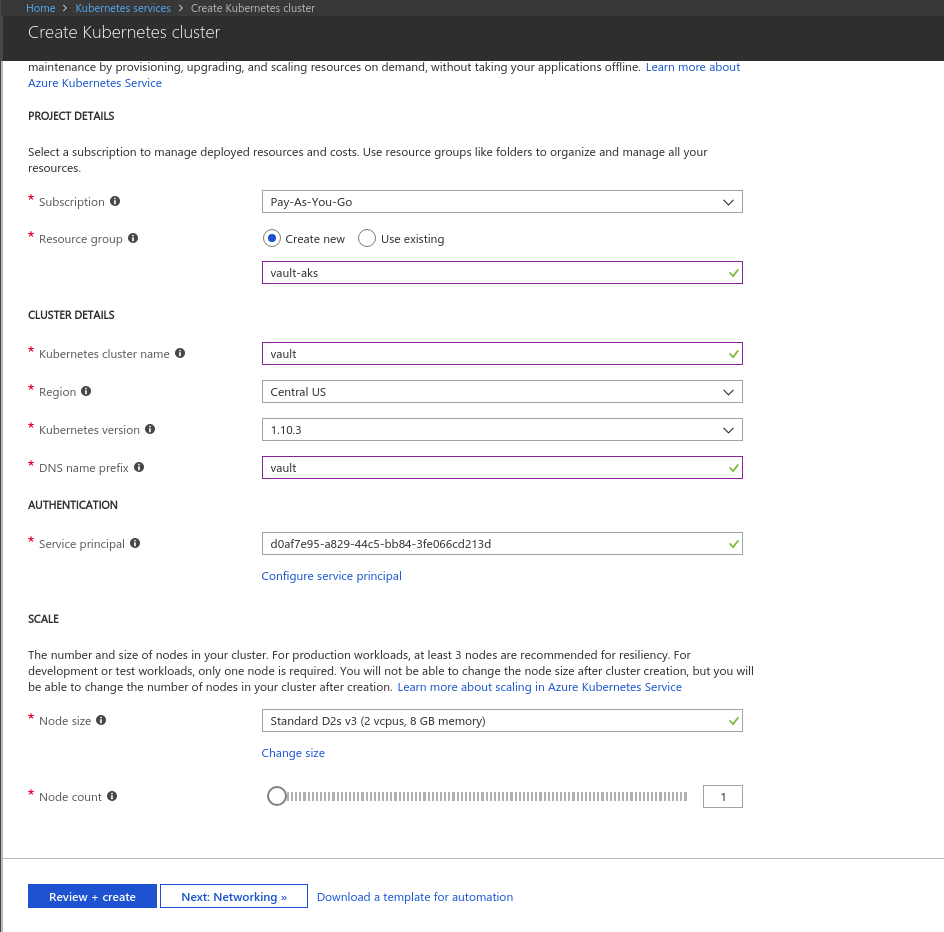
Configure .kube/config
$ az aks get-credentials --resource-group vault-aks --name vault
Merged "vault" as current context in /home/ac/.kube/config
$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system heapster-5d6f9b846c-69fvm 2/2 Running 0 47m
kube-system kube-dns-v20-7c7d7d4c66-8r7st 4/4 Running 0 48m
kube-system kube-dns-v20-7c7d7d4c66-vzg6n 4/4 Running 0 48m
kube-system kube-proxy-82c8t 1/1 Running 0 45m
kube-system kube-svc-redirect-hl6gz 2/2 Running 0 45m
kube-system kubernetes-dashboard-68f468887f-5knhd 1/1 Running 1 47m
kube-system metrics-server-5cbc77f79f-jc8b4 1/1 Running 1 47m
kube-system omsagent-rs-ddc44b8cd-m42b2 1/1 Running 0 47m
kube-system omsagent-s82s2 1/1 Running 0 45m
kube-system tunnelfront-8475548867-xvddt 1/1 Running 0 47m
We are going to create a web app/api type Azure Active Directory Application vault-app. Guides to create an Azure AD application can be found here. We will use the application id and key of this vault-app as credential. We are going to give vault-app application access to the secret in key vault vault-key-store.
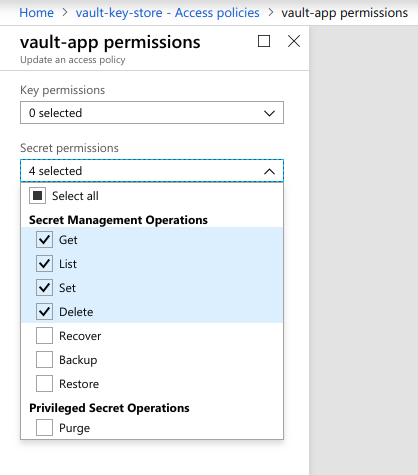
Install KubeVault operator
See here.
$ kubectl get pods -n kube-system
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system vault-operator-576b7867cb-tmz2j 1/1 Running 0 7m
Deploy Vault
To keep things isolated, we are going to use a separate namespace called demo throughout this tutorial.
$ kubectl create ns demo
namespace/demo created
We will deploy my-vault on demo namespace. We will configure it for Azure Container backend. We will use azureKeyVault for auto initializing and unsealing.
apiVersion: kubevault.com/v1alpha1
kind: VaultServer
metadata:
name: my-vault
namespace: demo
spec:
replicas: 1
version: "1.2.0"
backend:
azure:
container: demo-vault
accountName: vaultstorageac
accountKeySecret: azure-ac-key
unsealer:
secretShares: 4
secretThreshold: 2
mode:
azureKeyVault:
vaultBaseURL: https://vault-key-store.vault.azure.net/
tenantID: aaaaaaa-bbbb-ccc-dddd-eeeeeeeee
aadClientSecret: azure-ad-client-secret
Here, spec.version specifies the name of the VaultServerVersion CRD. If that does not exist, then create one.
$ kubectl get vaultserverversions
NAME VERSION VAULT_IMAGE DEPRECATED AGE
1.2.0 1.2.0 vault:1.2.0 false 1m
$ kubectl get vaultserverversions/1.2.0 -o yaml
apiVersion: catalog.kubevault.com/v1alpha1
kind: VaultServerVersion
metadata:
name: 1.2.0
spec:
version: 1.2.0
deprecated: false
vault:
image: vault:1.2.0
unsealer:
image: kubevault/vault-unsealer:v0.3.0
exporter:
image: kubevault/vault-exporter:0.1.0
spec.backend.azure.accountKeySecret specifies the name of the Kubernetes secret containing vaultstorageac storage account key.
$ kubectl get secrets azure-ac-key -n demo -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
account_key: QW5EOHhvQ1pWZ...
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: azure-ac-key
namespace: demo
type: Opaque
spec.unsealer.mode.azureKeyVault.aadClientSecret specifies the name of Kubernetes secret containing credential of vault-app Azure AD application.
$ kubectl get secrets azure-ad-client-secret -n demo -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
client-id: NzUw...
client-secret: clllWmNPd...
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: azure-ad-client-secret
namespace: demo
type: Opaque
spec.unsealer.mode.azureKeyVault.vaultBaseURL is the DNS name of the vault-key-store key vault.
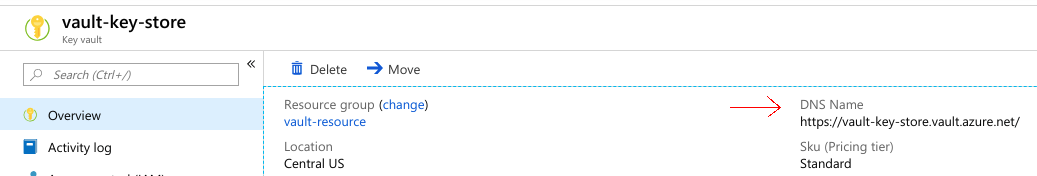
Now, we are going to create my-vault in demo namespace.
$ cat examples/guides/provider/aks/my-vault.yaml
apiVersion: kubevault.com/v1alpha1
kind: VaultServer
metadata:
name: my-vault
namespace: demo
spec:
replicas: 1
version: "1.2.0"
backend:
azure:
container: demo-vault
accountName: vaultstorageac
accountKeySecret: azure-ac-key
unsealer:
secretShares: 4
secretThreshold: 2
mode:
azureKeyVault:
vaultBaseURL: https://vault-key-store.vault.azure.net/
tenantID: aaaaaaa-bbbb-ccc-dddd-eeeeeeeee
aadClientSecret: azure-ad-client-secret
$ kubectl apply -f docs/examples/guides/provider/aks/my-vault.yaml
vaultserver.kubevault.com/my-vault created
Check the my-vault status. It may take some time to reach Running stage.
$ kubectl get vaultserver/my-vault -n demo
NAME NODES VERSION STATUS AGE
my-vault 1 1.2.0 Running 2m
status field in my-vault will show more detail information.
$ kubectl get vaultserver/my-vault -n demo -o json | jq '.status'
{
"clientPort": 8200,
"initialized": true,
"observedGeneration": "2$6206030548680361215",
"phase": "Running",
"serviceName": "my-vault",
"updatedNodes": [
"my-vault-684c485f7-7t6zs"
],
"vaultStatus": {
"active": "my-vault-684c485f7-7t6zs",
"unsealed": [
"my-vault-684c485f7-7t6zs"
]
}
}
KubeVault operator will create a service {metadata.name} for my-vault in the same namespace. For this case, service name is my-vault. You can specify service configuration in spec.serviceTemplate. KubeVault operator will use that configuration to create service.
$ kubectl get services -n demo
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
my-vault ClusterIP 10.3.244.122 <none> 8200/TCP,8201/TCP,9102/TCP 4m
The configuration used to run Vault can be found in {metadata.name}-vault-config configMap. For this case, it is my-vault-vault-config. Confidential data are omitted in this configMap.
$ kubectl get configmaps -n demo
NAME DATA AGE
my-vault-vault-config 1 49m
$ kubectl get configmaps/my-vault-vault-config -n demo -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
vault.hcl: |2-
listener "tcp" {
address = "0.0.0.0:8200"
cluster_address = "0.0.0.0:8201"
tls_cert_file = "/etc/vault/tls/tls.crt"
tls_key_file = "/etc/vault/tls/tls.key"
}
storage "azure" {
accountName = "vaultstorageac"
container = "demo-vault"
}
telemetry {
statsd_address = "0.0.0.0:9125"
}
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: my-vault-vault-config
namespace: demo
In this my-vault, KubeVault operator will use self-signed certificates for Vault and also will create {metadata.name}-vault-tls secret containing certificates. You can optionally specify certificates in spec.tls.
$ kubectl get secrets -n demo
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
my-vault-vault-tls Opaque 3 1h
We can see unseal keys and root token in vault-key-store key vault.
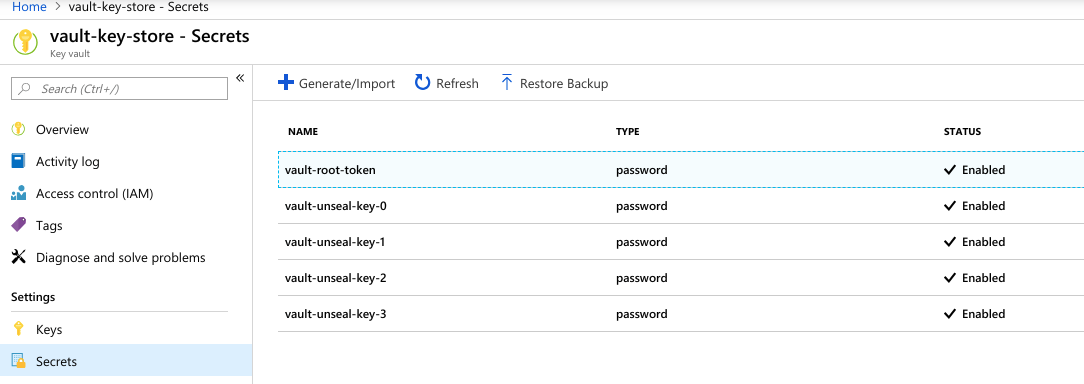
Using Vault
Collect the root token from vault-key-store:
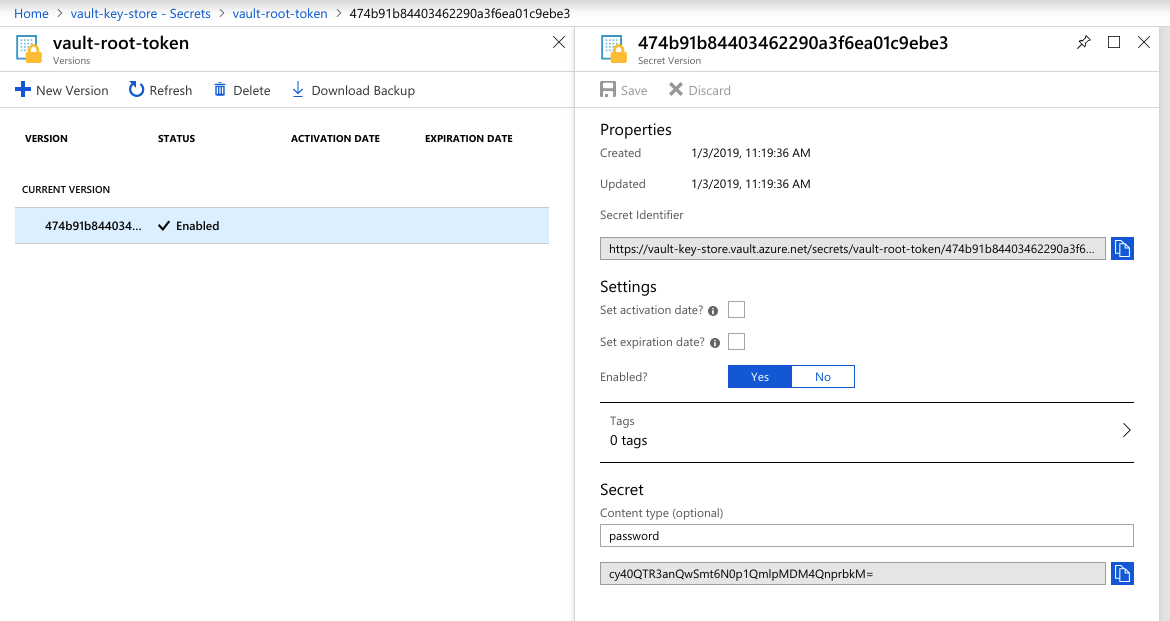
$ echo "cy40QTR3anQwSmt6N0p1QmlpMDM4QnprbkM=" | base64 -d
s.4A4wjt0Jkz7JuBii038BzknC
Note: Make sure you have the permission to do above operation. Also we highly recommend not to use root token for using vault.
For testing purpose, we are going to port forward the active vault pod, since the service we exposed for Vault is ClusterIP type. Make sure Vault cli is installed.
$ kubectl port-forward my-vault-684c485f7-7t6zs -n demo 8200:8200
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:8200 -> 8200
# run following commands on another terminal
$ export VAULT_SKIP_VERIFY="true"
$ export VAULT_ADDR='https://127.0.0.1:8200'
$ vault status
Key Value
--- -----
Seal Type shamir
Sealed false
Total Shares 4
Threshold 2
Version 1.2.0
Cluster Name vault-cluster-0650d1f5
Cluster ID 8a8ebf6a-a06a-0e79-cc74-a66d0d52df85
HA Enabled false
Set Vault token for further use. In this case, we are going to use root token(not recommended).
$ $ export VAULT_TOKEN='s.4A4wjt0Jkz7JuBii038BzknC'
$ vault secrets list
Path Type Accessor Description
---- ---- -------- -----------
cubbyhole/ cubbyhole cubbyhole_9ce16bb9 per-token private secret storage
identity/ identity identity_45904875 identity store
secret/ kv kv_22970276 key/value secret storage
sys/ system system_51cd4d05 system endpoints used for control, policy and debugging
We are going to write,read and delete a secret in Vault
$ vault kv put secret/foo A=B
Success! Data written to: secret/foo
# see written secret data
$ vault kv get secret/foo
== Data ==
Key Value
--- -----
A B
# delete the secret
$ vault kv delete secret/foo
Success! Data deleted (if it existed) at: secret/foo
# check the secret whether it is exist or not
$ vault kv get secret/foo
No value found at secret/foo






















