You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to KubeVault? Please start here.
Monitor Vault server with builtin Prometheus scraper
This tutorial will show you how to configure builtin Prometheus scraper to monitor Vault server provisioned by the KubeVault operator.
The prometheus server is needed to configure so that it can discover endpoints of Kubernetes services. If a Prometheus server is already running in cluster and if it is configured in a way that it can discover service endpoints, no extra configuration will be needed.Otherwise, read this tutorial to deploy a Prometheus server with appropriate configuration.
Create the following configmap with Prometheus configuration and pass it to a Prometheus server.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: prometheus-server-conf
labels:
name: prometheus-server-conf
namespace: demo
data:
prometheus.yml: |-
global:
scrape_interval: 5s
evaluation_interval: 5s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'kubernetes-service-endpoints'
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape]
action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme]
action: replace
target_label: __scheme__
regex: (https?)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path]
action: replace
target_label: __metrics_path__
regex: (.+)
- source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port]
action: replace
target_label: __address__
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $1:$2
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name]
action: replace
target_label: kubernetes_name
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_name]
action: replace
target_label: pod_name
You can create above ConfigMap by running
$ kubectl create -f https://github.com/kubevault/kubevault/raw/v2022.09.09/docs/examples/monitoring/vault-server/prom-server-conf.yaml
configmap/prometheus-server-conf created
Note: YAML files used in this tutorial are stored in docs/examples
Monitor Vault server
To enable monitoring, configure spec.monitor field in a VaultServer custom resource. Below is an example:
apiVersion: kubevault.com/v1alpha1
kind: VaultServer
metadata:
name: vault
namespace: demo
spec:
replicas: 1
version: 1.2.0
serviceTemplates:
- alias: vault
metadata:
annotations:
name: vault
spec:
type: NodePort
- alias: stats
spec:
type: ClusterIP
backend:
inmem: {}
unsealer:
secretShares: 4
secretThreshold: 2
mode:
kubernetesSecret:
secretName: vault-keys
monitor:
agent: prometheus.io
prometheus:
exporter:
resources: {}
terminationPolicy: "WipeOut"
Here,
spec.monitorspecifies that built-in prometheus is used to monitor this Vault server instance.monitor.prometheusspecifies the information for monitoring by Prometheus.prometheus.portindicates the port for Vault statsd exporter endpoint (default is56790)prometheus.intervalindicates the scraping interval (eg, ’10s')
Run the following command to create it.
$ kubectl create -f https://github.com/kubevault/kubevault/raw/v2022.09.09/docs/examples/monitoring/vault-server/vault-server-builtin.yaml
vaultserver.kubevault.com/example created
KubeVault operator will configure its service once the Vault server is successfully running.
$ kubectl get vs -n demo
NAME NODES VERSION STATUS AGE
example 1 0.11.1 Running 3h
Let’s describe Service example-stats
$ kubectl get svc -n demo example -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
annotations:
monitoring.appscode.com/agent: prometheus.io/builtin
prometheus.io/path: /metrics
prometheus.io/port: "9102"
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
creationTimestamp: "2018-12-24T11:27:28Z"
labels:
app: vault
vault_cluster: example
name: example
namespace: demo
ownerReferences:
- apiVersion: kubevault.com/v1alpha1
controller: true
kind: VaultServer
name: example
uid: e42c20cd-076e-11e9-b586-0800274de81b
resourceVersion: "1828"
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/demo/services/example
uid: e5064216-076e-11e9-b586-0800274de81b
spec:
clusterIP: 10.107.246.170
externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
ports:
- name: client
nodePort: 31528
port: 8200
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8200
- name: cluster
nodePort: 32245
port: 8201
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8201
- name: prom-http
nodePort: 30292
port: 9102
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 9102
selector:
app: vault
vault_cluster: example
sessionAffinity: None
type: NodePort
status:
loadBalancer: {}
You can see that the service contains following annotations.
monitoring.appscode.com/agent: prometheus.io/builtin
prometheus.io/path: /metrics
prometheus.io/port: "9102"
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
The Prometheus server will discover the Vault service endpoint and will scrape metrics from the exporter sidecar.
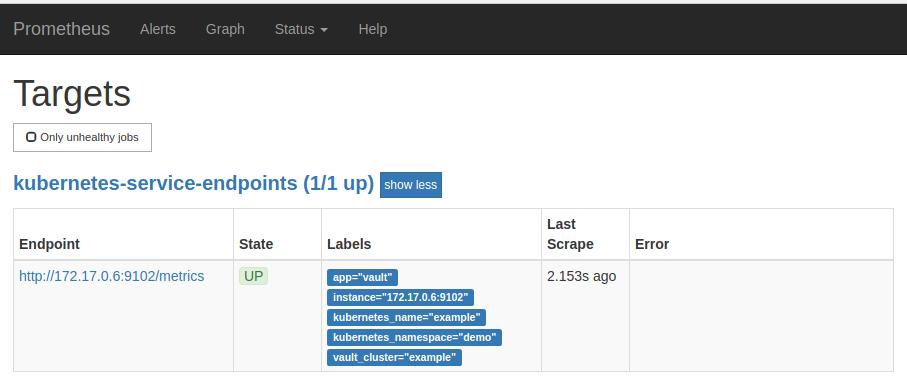
Cleaning up
To cleanup the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run:
$ kubectl delete -n demo vs/example
$ kubectl delete ns demo






















